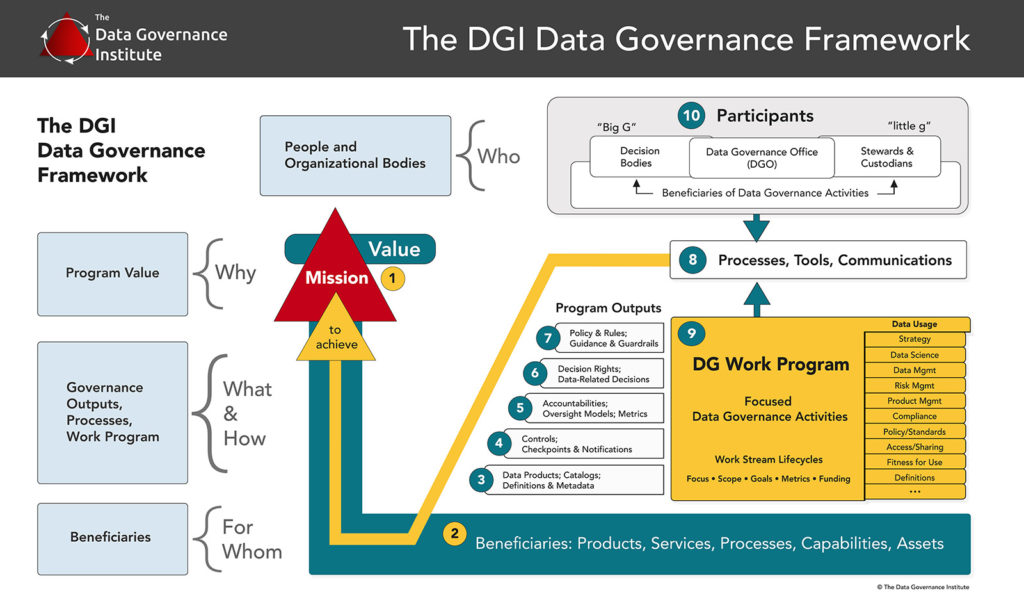
Who does what in a Data Governance program?
First, a group of individuals (or a hierarchy of groups) representing a cross-section of stakeholder groups makes a set of rules in the form of policies, standards, requirements, guidelines, or data definitions. (Or, they gather and align rules. Or address gaps and overlaps in rule sets. Or interpret rules. Or establish guidelines for how to layer rules on top of each other.)

This group of rule-makers may go by several names: a Data Governance Board, a Data Stewardship Council, etc. They may be self-organizing, or they may be called together by another body such as a Data Governance Office (DGO) that coordinates and facilitates efforts.
Next, Data Governance always includes a mechanism for resolving data-related issues. Issues are generally addressed at several levels, with a clear escalation path. A particular issue, then, may be resolved by an individual Data Steward, a Stewardship working group, the entire Data Stewardship Council, or the highest-level Data Governance Board.
Finally, the best Data Governance programs proactively strive to stop data-related problems before they begin by reducing ambiguity, establishing clear accountabilities, and disseminating data-related information to all Data Stakeholders. Such programs usually include a Data Governance Office (DGO) or its equivalent to provide alignment between stakeholders and to provide ongoing support to programs, projects, and groups that work with data.