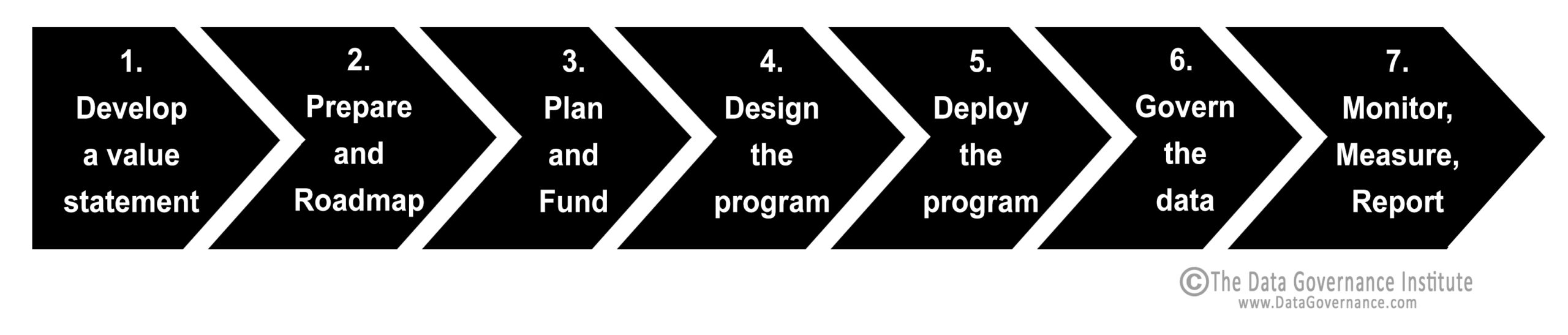
All programs have lifecycles. The Data Governance Life Cycle has seven phases:
- Develop a value statement
- Prepare a roadmap
- Plan and fund
- Design
- Deploy
- Govern
- Monitor, measure, report.
Note that Data Governance does not begin with the design of the program!
- Before you start deciding who goes on what committee, you should be clear about your program’s value statement.
- You should have developed a roadmap to share with stakeholders.
- Those stakeholders will want to know the WHO / WHAT / WHEN / WHERE / WHY / HOW of your program before they decide to support it, so you need to anticipate their questions. You’ll need preliminary answers, even if they’re only assumptions until you do your actual program design
As you perform the activities needed to gain support and funding, remember that your program may plan to address multiple focus areas. Each new effort should be introduced using the seven steps of the life cycle. Even specific governance-led projects, such as creating a set of data standards, will want to follow the Data Governance Life Cycle steps.
A note about the final phase in the Data Governance Life Cycle: Each time you consider a new set of activities, you’ll want to anticipate stakeholders’ expectations for monitoring efforts, measuring success, and reporting status. Your ability to deliver industry-standard metrics that satisfy stakeholders can be the difference between program activities that are chronically painful and those that become routine.
